ABORAS
A polarimetric sun-as-a-star telescope designed to achieve ultra-precise RV measurements of the Sun's integrated light combined with HARPS3, providing crucial benchmarks for exoplanet detection and stellar variability studies.
Project Overview
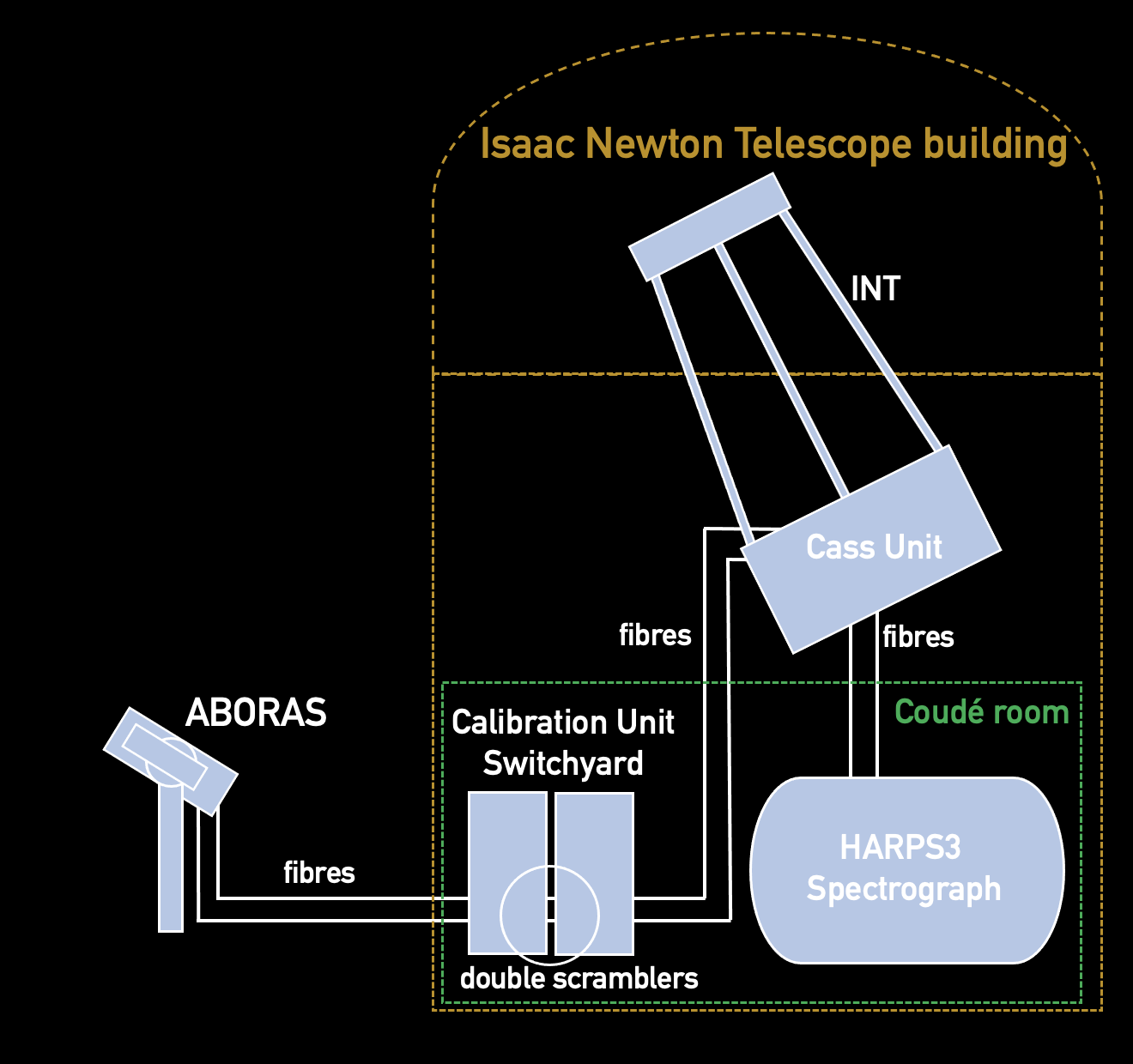
ABORAS (A dual-Beam polarimetric Robotic Aperture for the Sun) is a specialized solar telescope designed to feed sunlight into the HARPS3 high-resolution spectrograph. This instrument serves as an important tool for understanding stellar variability and its impact on exoplanet detection.
As a project lead, I was deeply involved in developing this instrument that combines polarimetric capabilities with precise radial velocity measurements. By observing the Sun as if it were a distant star, ABORAS provides invaluable insights into the limits of exoplanet detection techniques and helps refine our understanding of stellar activity.
Extreme Precision
Capable of measuring 10 cm/s variations in the radial velocity of the integrated solar disk, approaching the signal level of an Earth-like planet.
Polarimetric Analysis
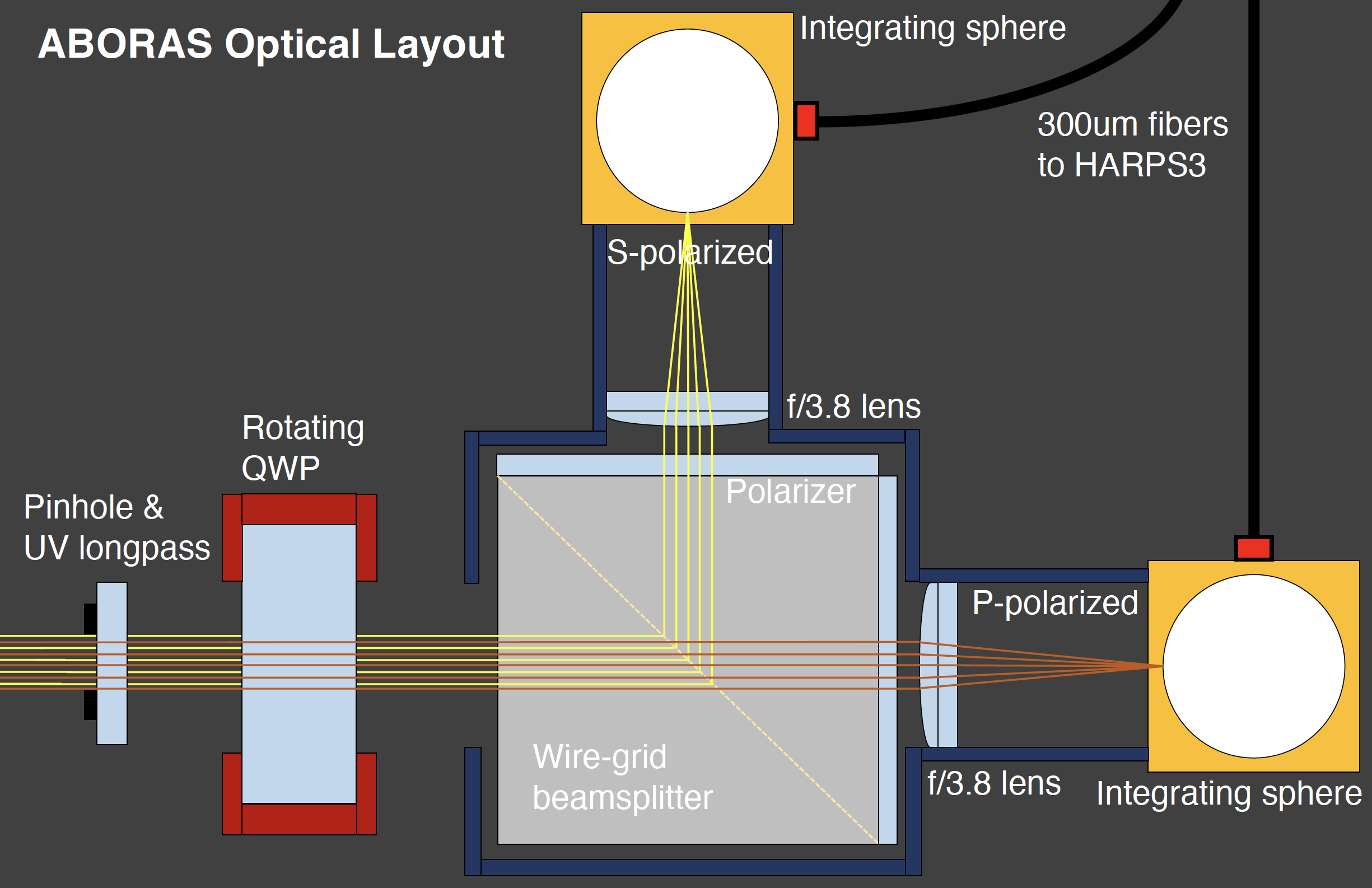
Equipped with a dedicated Stokes V polarimeter to detect integrated magnetic field levels below 1 Gauss through circularly polarized light.
Automated Operation
Fully robotic design for continuous monitoring of solar activity without human intervention, enabling long-term datasets.
Dual-Beam Design
Simultaneously collects perpendicularly polarized channels, allowing for precise reconstruction of the degree of circular polarization through the dual-beam exchange method.
Scientific Goals
Understanding Stellar Variability
By studying the Sun in RV and signed magnetic flux, ABORAS helps us understand the fundamental physics behind stellar activity and variability. This knowledge is essential for disentangling stellar signals from planetary signals in exoplanet searches.
Calibrating HARPS3 Stability
ABORAS serves as a continuous monitor of the long-term stability of the HARPS3 instrument, ensuring its reliability for detecting small exoplanets. This calibration is crucial for maintaining the 10cm/s RV precision required for Earth-like planet detection.
Earth-Sized Planet Detection Benchmarking
By injecting an Earth-like radial velocity signal into solar observations, ABORAS provides a realistic benchmark for testing detection methods. This approach allows us to determine the true limitations and capabilities of current and future exoplanet detection techniques.
System Design
Technical Specifications
| Specification | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RV Precision | 10 cm/s | Integrated solar disk measurement |
| Magnetic Sensitivity | < 1 Gauss | Through Stokes V polarimetry |
| Telescope Aperture | ~ 1 cm | Optimized for solar brightness |
| Spectral Resolution | ~ 115,000 | Via HARPS3 spectrograph |
| Wavelength Range | 380-690 nm | Optical range for stellar activity indicators |
| Automation Level | Fully Robotic | Including weather monitoring and safety systems |
Gallery
Related Publications
Contact
For more information about the ABORAS instrument or potential collaborations, please contact:
Annelies Mortier
Project Manager, ABORAS
Email: annelies.mortier@cambridge.ac.uk